What is mHealth?
mHealth or mobile health is the use of mobile phones and other wireless technology in medical care. These types of apps can be used for general health, fitness tracking, healthy eating and food monitoring to remote patient monitoring, consultations and disease management to name a few. The leading preference for health apps in the US currently is healthy eating.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines mHealth as medical and public health practice supported by mobile devices, such as mobile phones, patient monitoring devices, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and other wireless devices. And according to IQVIA the value of these tools typically derive from the ability to communicate information through the internet, web or text messaging, to provide continuous monitoring of human health metrics or display health data more clearly.
mHealth Apps Market
The mHealth apps market has grown rapidly over the last few years with the healthcare industry adopting new technologies. The global mHealth apps market was valued at $8bn in 2018 and is expected to generate $111.1bn by 2025.
North America accounts for the largest revenue share of the mHealth apps market at 40%. This is followed by Europe with Germany dominating the European mHealth apps market with a revenue share of 30%
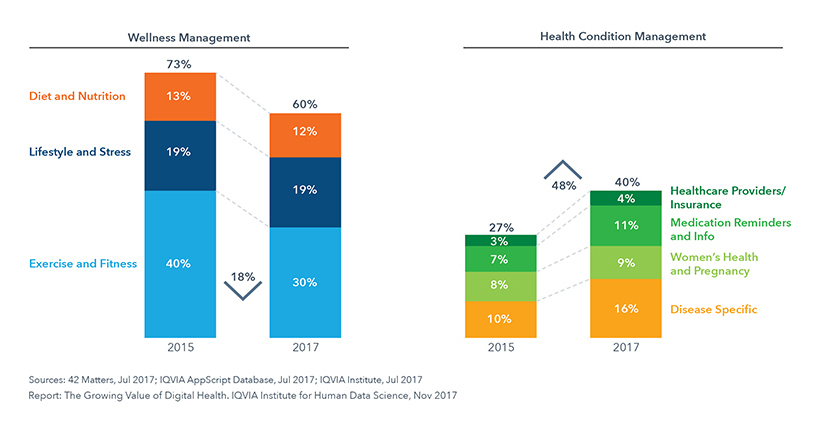
There are more than 318k health apps available worldwide with 200 health apps being added to the app stores daily. The majority of mobile health apps available are wellness apps. However, the number of health condition management apps (those associated with patient care) are increasing at a faster rate and now represent 40% of all health-related apps. And there is at least one high-quality app for each stage of the patient journey.
There are 571 published studies identifying a list of the top medical apps with robust clinical evidence. The use of healthcare apps in 5 patient studies could save the US healthcare system $7 billion per year. If this approach was adopted across national health expenditure, $46 billion could be saved annually. And you can imagine the figure if this was applied globally.
There are 540 current clinical trials in the US using mHealth technology and an estimated 20% of large health systems shifting from pilot digital health programs to full-scale rollouts.
Digital Health Apps by Category (2017)
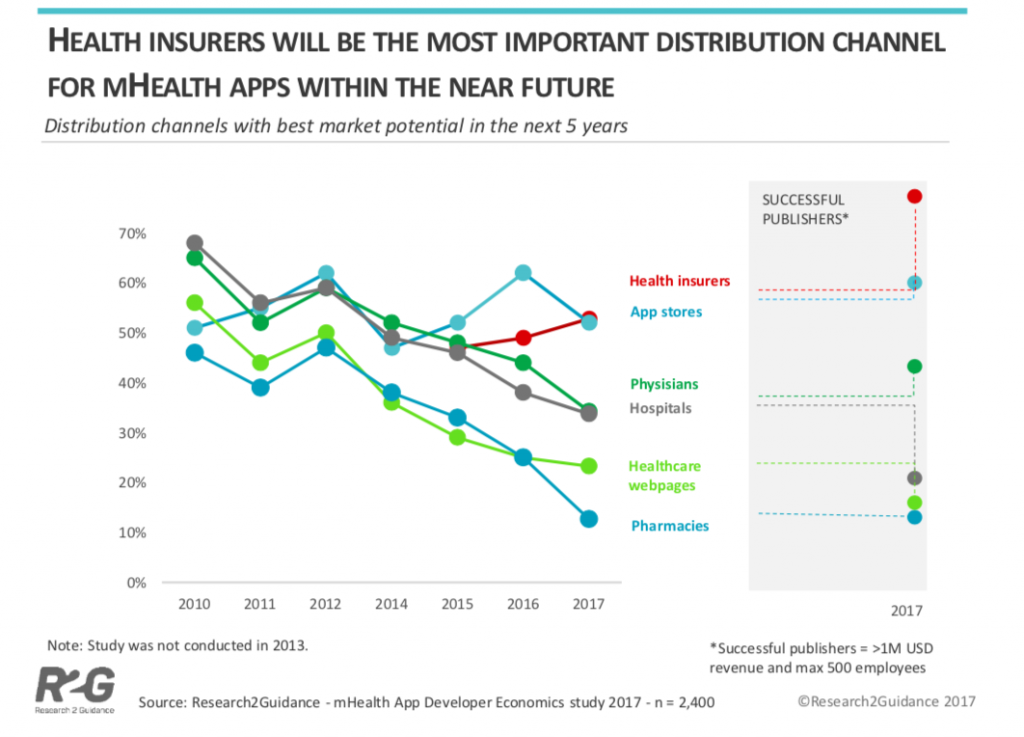
Market Potential
There are 84,000 health app publishers globally and a recent study found that 53% of digital health practitioners expect health insurers to be the future number one distribution channel with best market potential.
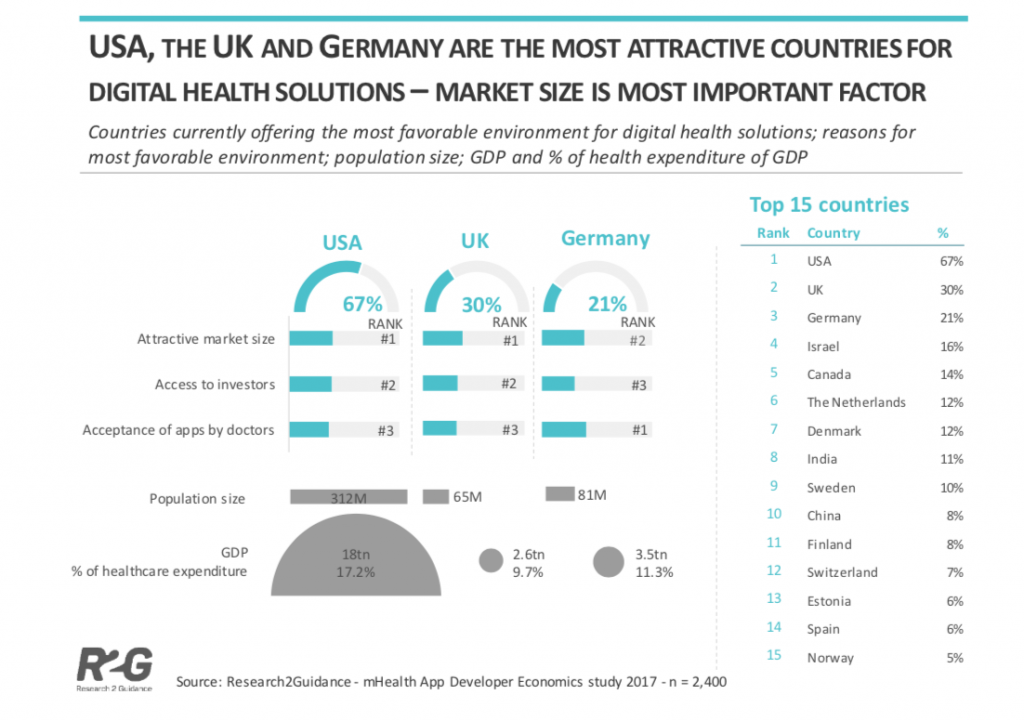
The countries with the best market conditions for digital health solutions are the USA, the UK and Germany because of their attractive market size, access to investors and acceptance of apps by doctors.
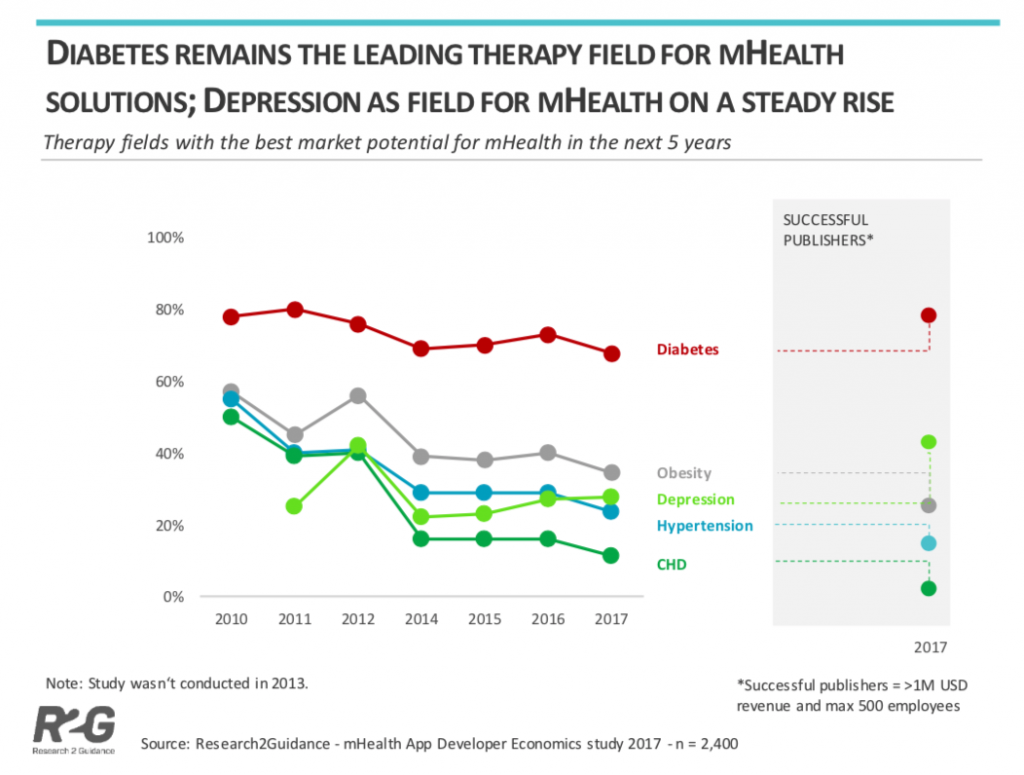
As diabetes is becoming a major problem in the US many healthcare professionals believe that mHealth apps relating to diabetes will have the greatest market potential.
Disease-Specific Apps by Therapy Area
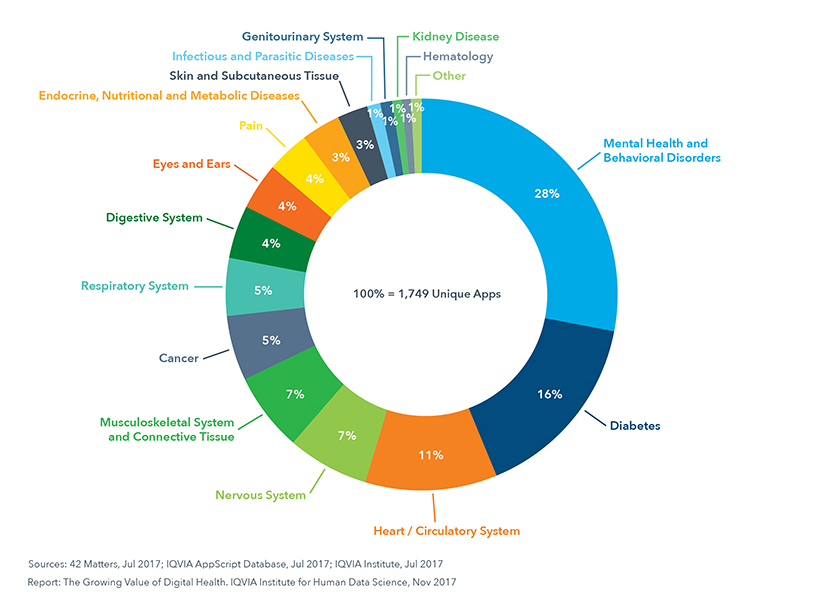
Research2Guidance have also identified diabetes as the leading therapy field for mHealth solutions.
Adoption of Digital Health Tools
According to a Rock Health survey 87% of respondents have adopted at least one digital health tool.
Some of the most popular digital health tools are online patient portals, secure text message, telemedicine, mobile clinical decision support services and online provider communities.
In a 2017 CDW survey 75% of patients are using an online patient portal provided by a healthcare provider. Patients can now easily make appointments and request prescription refills via an online patient portal.
Mobile phones are the preferred way of communicating today and many health care providers are taking advantage of using secure text message to send appointment reminders.
Telemedicine is becoming an increasingly popular digital health tool that patients are happy to use. Many of the health care insurers provide it as an added benefit to policies. Telemedicine makes it easy and convenient for patients to be seen and offers minimum disruption to their day.
Mobile clinical decision support services are becoming increasing popular among GP’s who find it impossible to know the side effect of every drug available. These types of support services improve the quality of care for patents.
Online provider communities are creating mobile apps for their networks to make it easier for GP’s to stay connected and to stay up to date with the latest trends and techniques.
Digital Health Tools

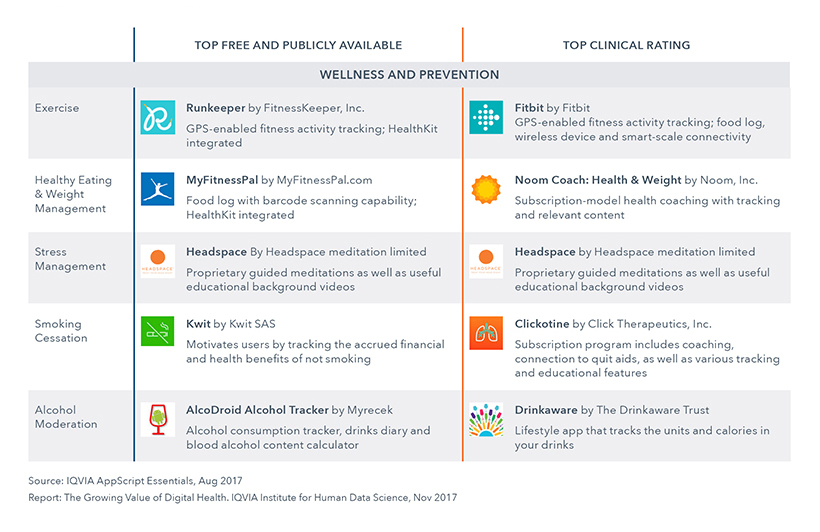
Top Rated Apps - Wellness & Prevention
IQVIA looked at the top apps for wellness and prevention across 15 high priority digital health app categories with high app demand and app quality. The categories are split by Free and Publicly Available and Clinical Rating. 80% of these apps have at least one positive observational study demonstrating clinical efficacy. More than half connect to an external sensor directly or via a hub such as Apple HealthKit.
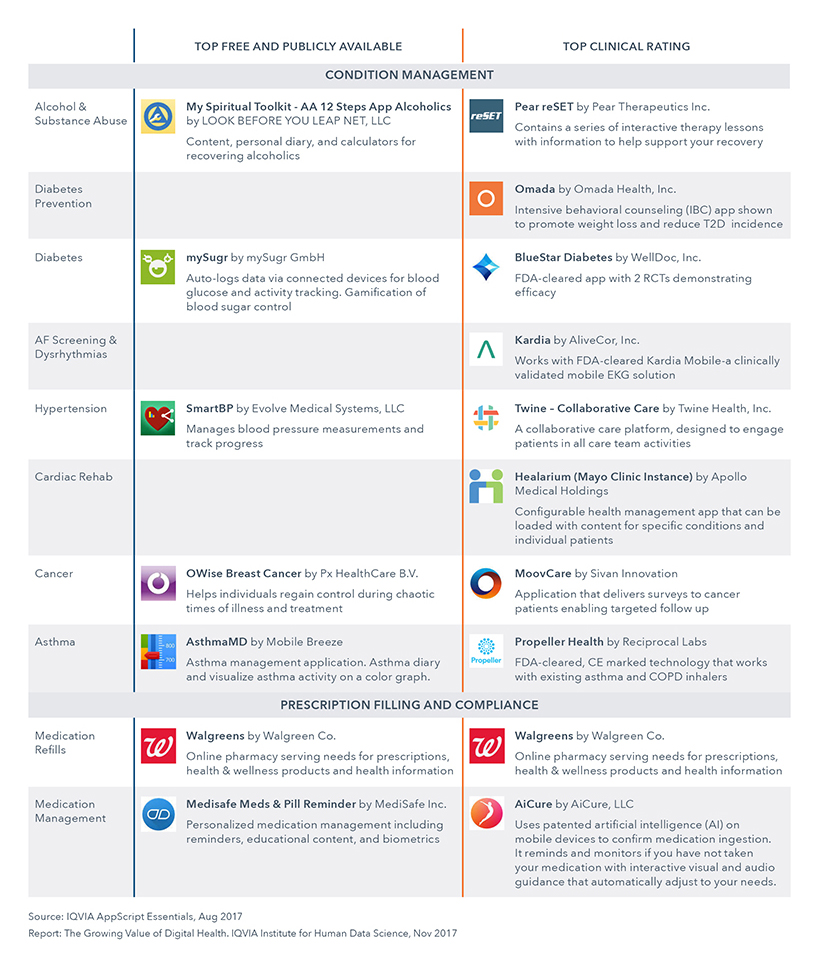
Top Rated Apps - Condition Management
A look at Ireland
The healthcare and life sciences sector is one of Ireland’s strongest business sectors. The total life science sector across medical devices, Pharma and bio in Ireland exports more than €45 billion annually and employers over 50k people directly. It has operations from six of the top seven diagnostics companies.
Ireland is the largest employer of medtech professionals in Europe per capita. It employs 38,000 people in over 350 companies. It is also the second-largest exporter of medtech products in Europe, with annual exports of €12.6 billion to over 100 countries globally.
The Irish medical device sector has 160 companies and employs more than 24k people. It generates sales in excess of €6 billion and has operations from eight of the 10 world’s largest medical device companies. The big international players with substantial Irish operations include Abbott, Bayer, Becton Dickinson, Boston Scientific, Johnson & Johnson, Guidant, Medtronic and Stryker.
Ireland’s largest home-grown medical device company Creganna/Tactx employers over 800 people world-wide and provides a range of contract manufacturing and contract R&D services to start-ups and global companies alike.
The Future Outlook for Ireland
Ireland has a world-leading position in the medtech sector. This is set to be maintained with Muiris O’Connor, the Department of Health’s assistant secretary at R&D and Health Analytics Division telling a recent Enterprise Ireland-hosted conference on the eHealth Ireland EcoSystem that a clear funding pathway for eHealth has been secured. €85 million in funding was secured for 2019, €100 million for 2020 and €120 million for 2021.
Deloitte has noted in their 2019 Global Life Sciences Outlook that software is changing how clinicians practice medicine, how consumers manage their own health, and how patients and providers interact. Software as a medical device (SaMD) is a software that provides one or more medical functions and is usually embedded in hardware.
A key point from their report is that in this highly digitized and connected world where patients have complete visibility into the experience they will be provided, it is imperative for companies to double the focus on customer experience. Companies should prioritize interpreting the burden of a disease on specific groups by building a culture where patients are partners, and not just consumers. Advanced technologies like AI can play a critical role here by helping pharma companies produce highly personalized solutions at competitive prices within shorter durations. Integrating connected medical devices into existing care pathways require collaboration across the IoMT ecosystem that can be facilitated by partnerships and joint ventures.
Conclusion
As the mHealth apps market continues to grow, so too does uncertainty around which apps are suited to one’s particular needs. There’s also skepticism amongst consumers and clinicians in relation to security and privacy of user information.
The US Food and Drug Administration sent a warning recently advising the public not to use unapproved or uncleared medical devices to help assess or diagnose a concussion. These smartphone apps are being marketed to coaches and parents for use during sporting events. According to the FDA “…have not been reviewed by the FDA for safety and efficacy and could result in an incorrect diagnosis, potentially leading to a person with a serious head injury returning to their normal activities instead of getting medical care”.
Of the hundreds and thousands of mHealth apps on the market only 22 have been evaluated in the last decade.
There’s huge potential in the mHealth apps market, but in order for it to realise it’s true potential publishers need to establish value and trust amongst consumers and investors.
Maria Colgan
Thanks for reading the Tapadoo blog. We've been building iOS and Android Apps since 2009. If your business needs an App, or you want advice on anything mobile, please get in touch
